HANA News Blog
Dynamic Range Partitioning - Interval Option
Dynamic range partitioning - option 2
Interval option
The interval option was introduced with SPS06 and can be used if you exactly know how the data will be distributed. Mostly it is used for time range partitioning. It operates like the threshold option on top of the OTHERS partition. It can currently only add partitions on base of the last range. It can not add a range before a already existing range. You can define a time interval based on month, year and hour. Currently an interval based on day or week is no possible by using this syntax. The target field for partitioning must be a real datetime type otherwise you have to use the integer option. The integer option will be used by default if no signal word like MONTH, YEAR or HOUR is used. It can be perfectly used for number ranges if you know how many distinct values represents a certain partition size. This means if you know that 50,000 values (not records!) of an attribute representing 250,000,000 - 500,000,000 records or a partitions size of 25 - 50GB than you may can use it as an integer interval to create automatically a right sized new partition. But use it with the needed care, there are a lot of pitfalls.
Prerequisites
partition schema: RANGE
type of partitioning: heterogenous
supported data types: DATE, TIMESTAMP, SECONDDATE, NVARCHAR,VARCHAR, TINYINT, SMALLINT, INTEGER, BIGINT, SHORTTEXT
partitioning and definition based on complete lengths of the fields
no type definition using INTERVAL means: INT
With the INTERVAL option there are two ways of measuring time: either as a time value (using data types such as DATE, TIMESTAMP, SECONDDATE - see the second example below) or, because time intervals are not always equidistant (for example, a month may have between 28 and 31 days), the option of using a numerical counter is supported (using data types such as INT, BIGINT, NVARCHAR).
Example for a datetime field
Alter table example PARTITION by RANGE (YEAR(GJAHR)) ((
PARTITION 0000 <= VALUES < 2021,
PARTITION 2021 <= VALUES < 2022,
PARTITION 2022 <= VALUES < 2023,
PARTITION 2023 <= VALUES < 2024,
PARTITION 2024 <= VALUES < 2025,
PARTITION 2025 <= VALUES < 2026,
PARTITION OTHERS DYNAMIC INTERVAL 1 YEAR));
=> In this example the field GJAHR is of type date
=> If one row will be entered with GJAHR "2026" or more, a new partition will be created with range 1 year as soon as the background job successfully finished
Example for a SAP table
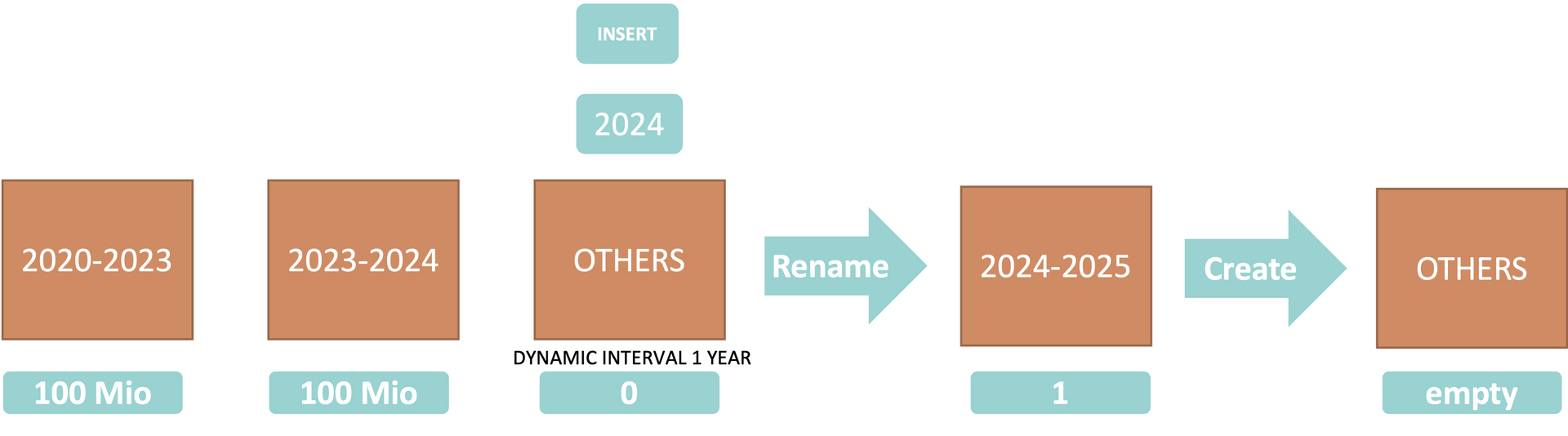
Alter table FAGLFLEXA PARTITION by RANGE (BUDAT) ((
PARTITION 00000000 <= VALUES < 20230101,
PARTITION 20230101 <= VALUES < 20240101,
PARTITION 20240101 <= VALUES < 20250101,
PARTITION OTHERS));
Alter table FAGLFLEXA ALTER PARTITION OTHERS DYNAMIC INTERVAL 10000;
It can be defined also in one step:
Alter table FAGLFLEXA PARTITION by RANGE (BUDAT) ((
PARTITION 00000000 <= VALUES < 20230101,
PARTITION 20230101 <= VALUES < 20240101,
PARTITION 20240101 <= VALUES < 20250101,
PARTITION OTHERS DYNAMIC INTERVAL 10000));
=> In this example the field BUDAT is of type NVARCHAR and the default type will be INT
=> If one row will be entered with BUDAT "2025mmdd" or more, a new partition will be created with range 10,000 as soon as the background job successfully finished
Deactivation
ALTER TABLE FAGLFLEXA ALTER PARTITION OTHERS NO DYNAMIC;
Usage for NVARCHAR SAP time fields
In the SAP universe there are no real datetime fields. This means we have to use what we have:
- 4 chars like GJAHR
- 6 chars like BUDAT
- 14 chars like KDATU
- 21 chars like TIMESTAMP
Known Issues
[7]:feature not supported: Dynamic interval is not supported for non-HETEROGENEOUS partitioning type
=> only usable with heterogenous partitioning type
[2048]: columns store error: alter others partition: [2051] Function should be set and consistent with dynamic interval type when dynamic interval property is used
=> If the syntax MONTH | YEAR | HOUR was used, the column must be of type datetime.
[2048]: columns store error: fail to alter partition: [2051] partition specification not valid; invalud integer-like range: Length of bound 'xxxx' is not equal to the length 14 of the partitioning column. Make sure to fill up the bound with '0' from the left until the required size is reached.
=> be careful by using the hint of this error. If you specified only 4 chars while needing 8 chars you should not fill up with '0' from the left:
'2024' => NOT '00002024' !!!
'2024' => correct '20240101'
column store error: add dynamic range: [2594] SAPSID::SCHEMA:TABLE: Attempting to generate too many partitions, exceeding the configured maximum partitions count 1000. Please check the configuration partitioning::max_partitions_generated_by_dynamic_range (default: 1000). The interval granularity is probably not suitable, or consider modifying the configuration if necessary.
=> the background job was triggered and would have add >1000 new partition which indicated an error, because this is not a normal behavior to add such a high number of partitions. I think even 1000 is quite a high default the parameter max_partitions_generated_by_dynamic_range. This can be the case if your data includes rows with the year 9999. This is often the case for price conditions in table PRCD_ELEMENTS.
[7]:feature not supported: HETEROGENEOUS Dynamic Range others partition cannot have subpartitions
=> with multilevel partitioning the OTHERS partitioning can also have subpartitions - this is not suitable using dynamic partitioning. Remove the subpartitions of OTHERS or you cannot use the interval option
Dynamic interval partitioning does not allow gaps between ranges. Found lower bound 19700101 but the upper bound of the previous range is 00000000 : Partition specification is invalid
=> please always check your MIN and MAX values - there must be no gaps if the feature is to be used
column store error: add dynamic range: [2594] Encounter non-integer value in partition OTHERS
=> check your master data - there is something wrong with your data or you have selected the wrong field
Pitfalls interval option
Be aware that if you are running a SAP system on top of HANA you have no real date data types. This means you have to work with integer values and cannot use the interval type value YEAR, MONTH or HOUR!
In a multi level partitioning it can only used at the first level if the others partitioning has no sub partitions.
If you have a yearly partitions and the process allow to enter the year 9999 your design will not work because a lot of empty partition would be created. For this reason check always the minimum and maximum values before you activate it!
The feature currently (SPS08) does not allow gaps between ranges (see the error section above) and new partitions can only be created at the end of a range.
How you can check if interval option is active?
SELECT TABLE_NAME, DYNAMIC_RANGE_INTERVAL from TABLE_PARTITIONS
Summary
The interval option is must have for big systems with RANGE partitioning and multiple partitions. There are a lot of limitations but may be SAP will improve this feature more and more.
Are you still adding your partitions manually? Automate it if possible to avoid unnecessary hassle. If you want to play it safe and not try it on your own, please contact us. It is better to be safe than sorry!
SAP HANA News by XLC