HANA News Blog
ACDOCA - central element in S/4 HANA
Jens Gleichmann • 10. Dezember 2024
ACDOCA table growth - how to handle it

Anyone dealing with S/4HANA heard about universal journal and the table ACDOCA. It is one central element of the S/4HANA simplification and also one of the largest and fastest growing tables.
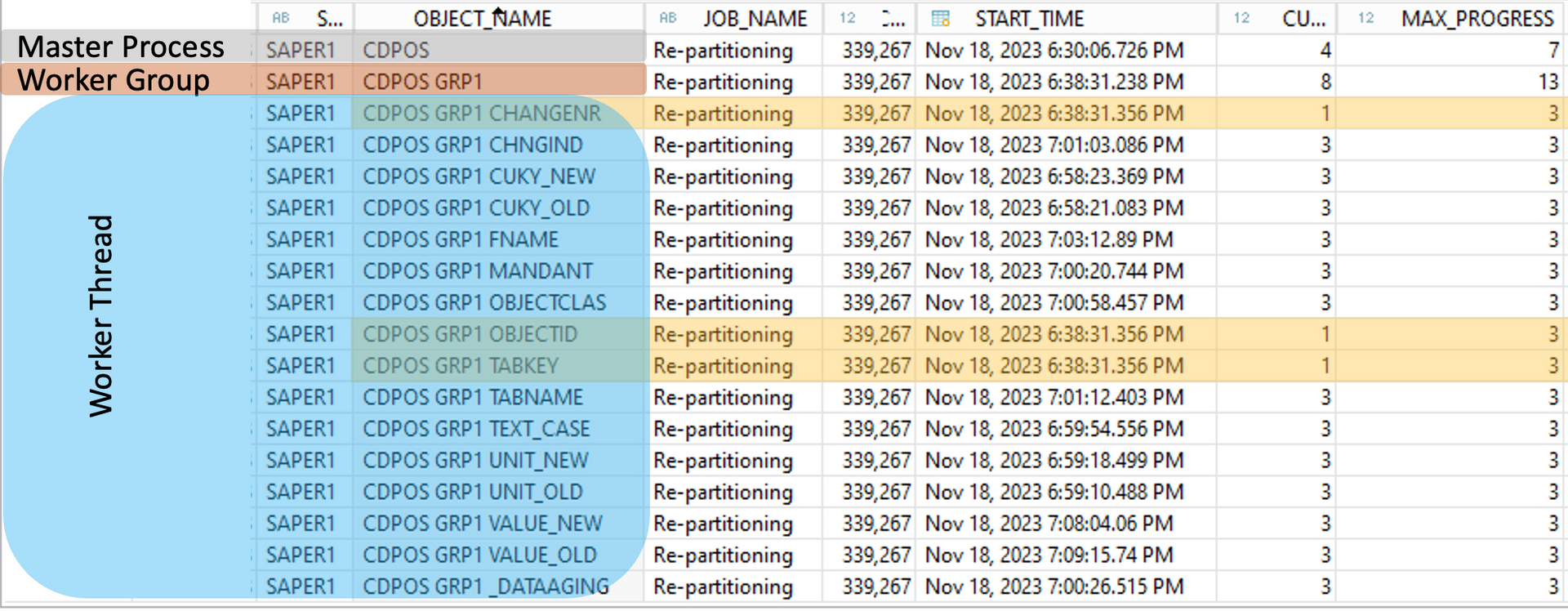
Due to this fact I had to deal with it 2 years ago in the context of data tiering (NSE). The tables had 448 columns
with the release S/4HANA 1909. SAP warned to use NSE for central complex tables, but the customer was brave enough to test it with Capture&Replay before going live with it. We achieved with our NSE design an average saving rate of 23% (max. 38%) of the table size.
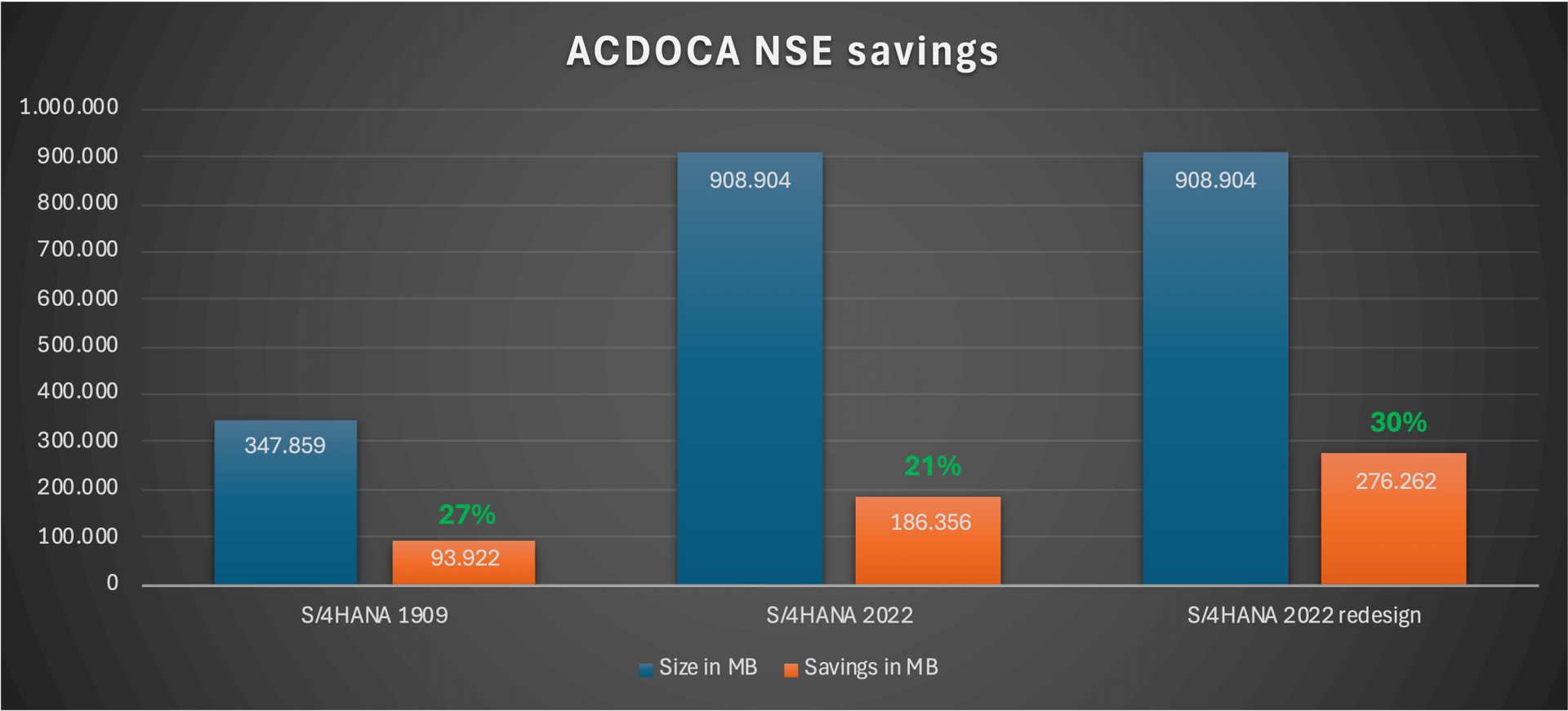
2 years later we are reviewing this design again and I wondered about the size and the low saving rate. The customer updated to S/4HANA 2022
and has now 494 fields! This means 46 additional fields. Over the years the releases received several new default fields and sometimes also customer extensibilities (SAP Note 2453614).
There are some kind of "What's New in SAP S/4HANA xxxx" documents, but they are not covering all changes regarding all new fields. The new fields are also responsible for a 5% higher growth and of course the lower NSE saving rate.
I started to figure out which field was introduced with which release but the documentation is about such details is a mess:
S/4HANA 1909 ACRVALDAT
S/4HANA 2020 FIPEX
S/4HANA 2021 CBTTYPE RFCCUR FCSL
S/4HANA 2022 AUFNR_ORG VORNR_ORG
We analyzed the new SQLs running against ACDOCA and the new fields. We adapted our strategy and could eleminate 93% of the new not considered growth. This means not 5% growth rather 0,35%. This small number might not impress but if the table has a size of over 400GB and you save 80 or 100GB it matters. If you also consider other big tables for NSE like PRCD_ELEMENTS or CDPOS you can save multiple 100GBs which will save hardware costs, license / maintenance costs. In our case our first ACDOCA NSE design was very conservative to hold the performance impact as low as possible. With our new design we are more aggressive but always with a trade-off in mind. We increased out savings from 21% to 30%. This means for this system about 280GB savings.
In the end nothing speaks against NSE with ACDOCA.
Keep in mind: You should always combine NSE with archiving, but this is not possible in all scenarios.
SAP HANA News by XLC

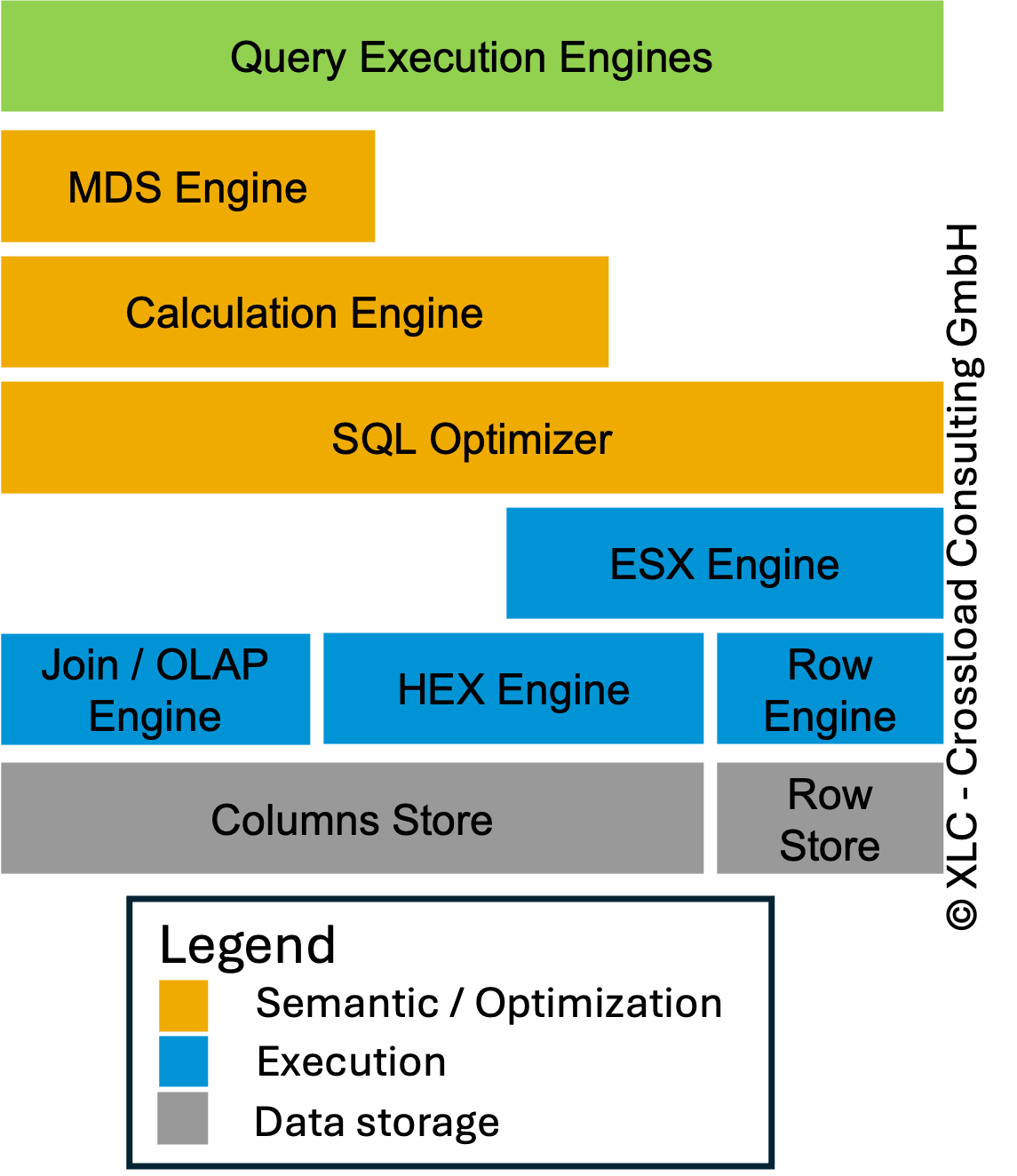
With SPS06 and even stronger in SPS07 the HEX engine was pushed to be used more often. This results on the one hand side in easy scenario to perfect results with lower memory and CPU consumption ending up in faster response times. But in scenarios with FAE (for all entries) together with FDA (fast data access), it can result in bad performance. After some customers upgraded their first systems to SPS07 I recommended to wait for Rev. 73/74. But some started early with Rev. 71/72 and we had to troubleshoot many statement. If you have similar performance issues after the upgrade to SPS07 feel free to contact us! Our current recommendation is to use Rev. 74 with some workarounds. The performance degradation is extreme in systems like EWM and BW with high analytical workload.
SAP NSE was introduced with HANA 2.0 SPS04 and based on a similar approach like data aging. Data aging based on a application level approach which has a side effect if you are using a lot of Z-coding. You have to use special BADI's to access the correct data. This means you have to adapt your coding if you are using it for Z-tables or using not SAP standard functions for accessing the data in your Z-coding. In this blog we will talk about the technical aspects in more detail.

In transformation projects like SAP RISE / SAP Cloud ERP, the Roles & Responsibilities (R+R) list often serves as the backbone for collaboration between customer, partner, and SAP. Yet too often, this list is treated as a static document rather than a living framework. Sometimes nobody knows exactly what was defined by
In the world of modern database management systems, query performance is not just a matter of hardware—it’s about smart execution plans. At the core of generating these plans lies a critical component: optimizer statistics.
This article explores why databases need optimizer statistics, with particular emphasis on SAP HANA, while drawing parallels with Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server (MSSQL), and IBM DB2.
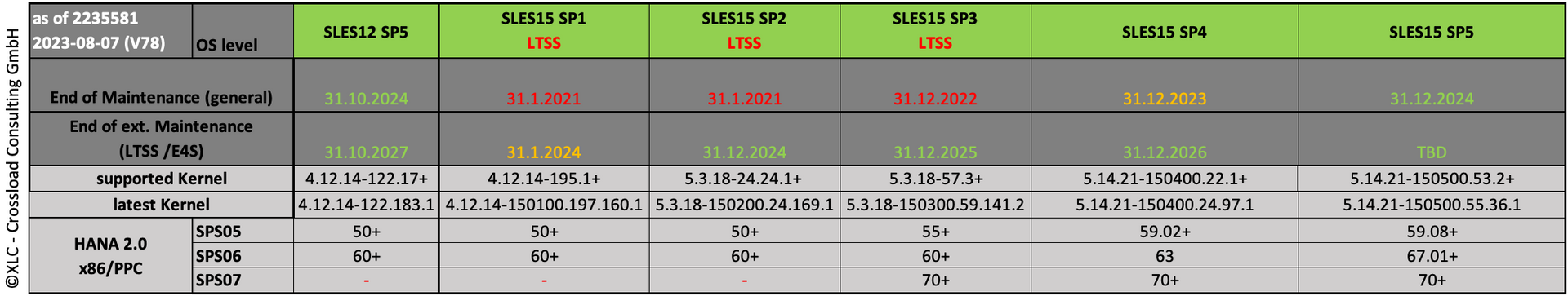
Please notice that when you want to run HANA 2.0 SPS07, you need defined OS levels. As you can see RHEL7 and SLES12 are not certified for SPS07. The SPS07 release of HANA is the basis for the S/4HANA release 2023 which is my recommended go-to release for the next years. Keep in mind that you have to go to SPS07 when you are running SPS06 because it will run out of maintenance end of 2023.
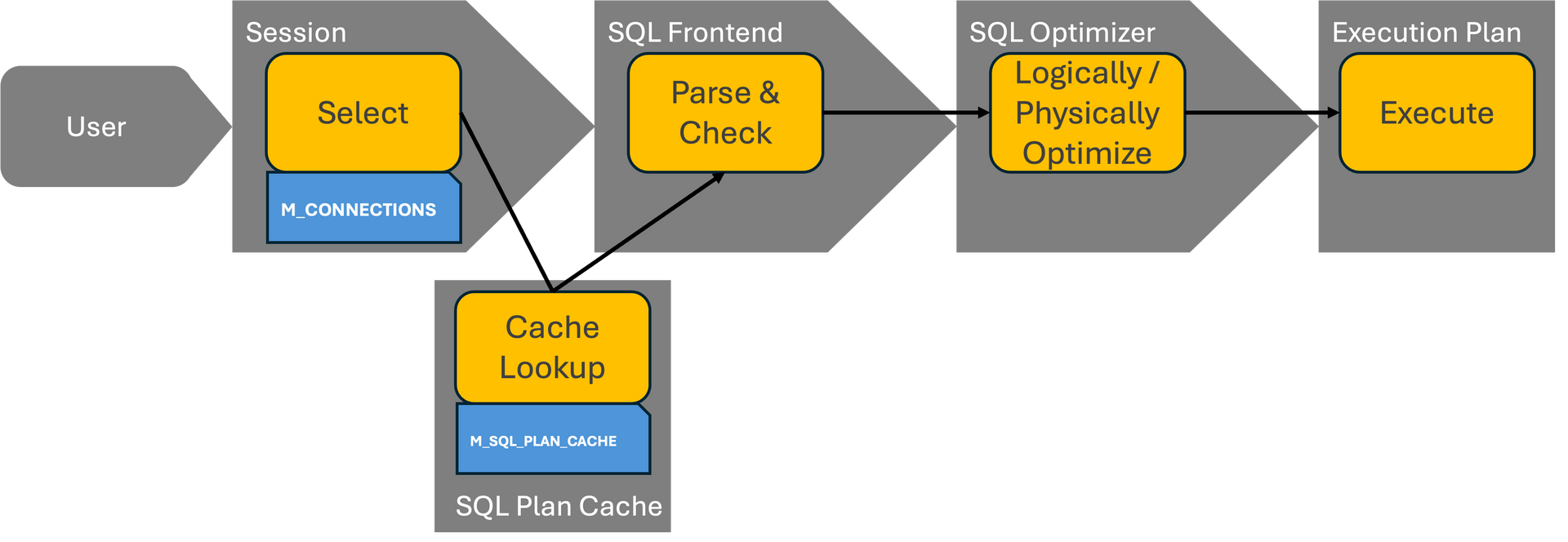
A database optimizer behaves similarly to the navigation system in your car. You use various parameters to determine which route you want to take to reach a particular destination. Potential additional costs for tolls and ferries also play a role, as do other limitations such as the vehicle's height, length, and width. From these input parameters, the navigation system determines the optimal route based on current traffic information (traffic volume, construction sites, congestion, accidents, closures, etc.), weather conditions, and the length of the route. This means that with exactly identical input parameters, different routes, costs, and thus different travel times can arise depending on the given conditions.
Most of our presentations on data tiering projects end with these typical questions:
How much we will save?
How fast can it be implemented?
Is the effort worth it over time?
My counter question:
"Do you know how much 1 GB of memory costs your company per month or year?"
=> how much memory we have to save to be beneficial?

Recently handelsblatt released an article with a new SAP RISE option called SAP ERP, private edition, transition option. This option includes a extended maintenance until the end 2033. This means 3 years more compared to the original on-prem extended maintenance. This statement was confirmed by SAP on request of handelsblatt, but customers receive more details, such as the price, in the first half of the year. This is a quite unusual move of SAP without any official statement on the news page. Just to raise more doubts? Strategy? However a good move against the critics and the ever shorter timeline. Perhaps it is also a consequence of the growing shortage of experts for operating and migrating the large number of systems.